Muse Stem Cell Therapy: A Revolutionary Step in Regenerative Medicine
Written by Dr. David Greene, MD, PhD, MBA on December 14, 2025
The US Leader in Stem Cell Therapy, Now in Mexico. Treatments start at $3750 for 25 million stem cells!
Special Promo: Get an additional 25 BILLION Exosomes IV with treatments over 50 million cells!”
The US Leader in Stem Cell Therapy, Now in Mexico. Affordable treatments start at $3750 for 25 million stem cells!
Special Promo: Get an additional 25 BILLION Exosomes IV with treatments over 50 million cells!”
Written by Dr. David Greene, MD, PhD, MBA on December 14, 2025
Stem cell therapy has been a buzzword in medical circles for quite some time now, with exciting breakthroughs offering hope for those struggling with conditions that once seemed untreatable. But have you ever heard of Muse stem cell therapy? If not, you’re in for a treat—this therapy is gaining traction and showing promising results in treating everything from stroke to heart attacks, spinal injuries, and more. But what exactly are Muse cells, and why should we be so excited about them?
In this article, we’re going to dive into what Muse stem cell therapy is, where these cells come from, how they differ from other stem cells like mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), and how they might just be the next big thing in regenerative medicine.
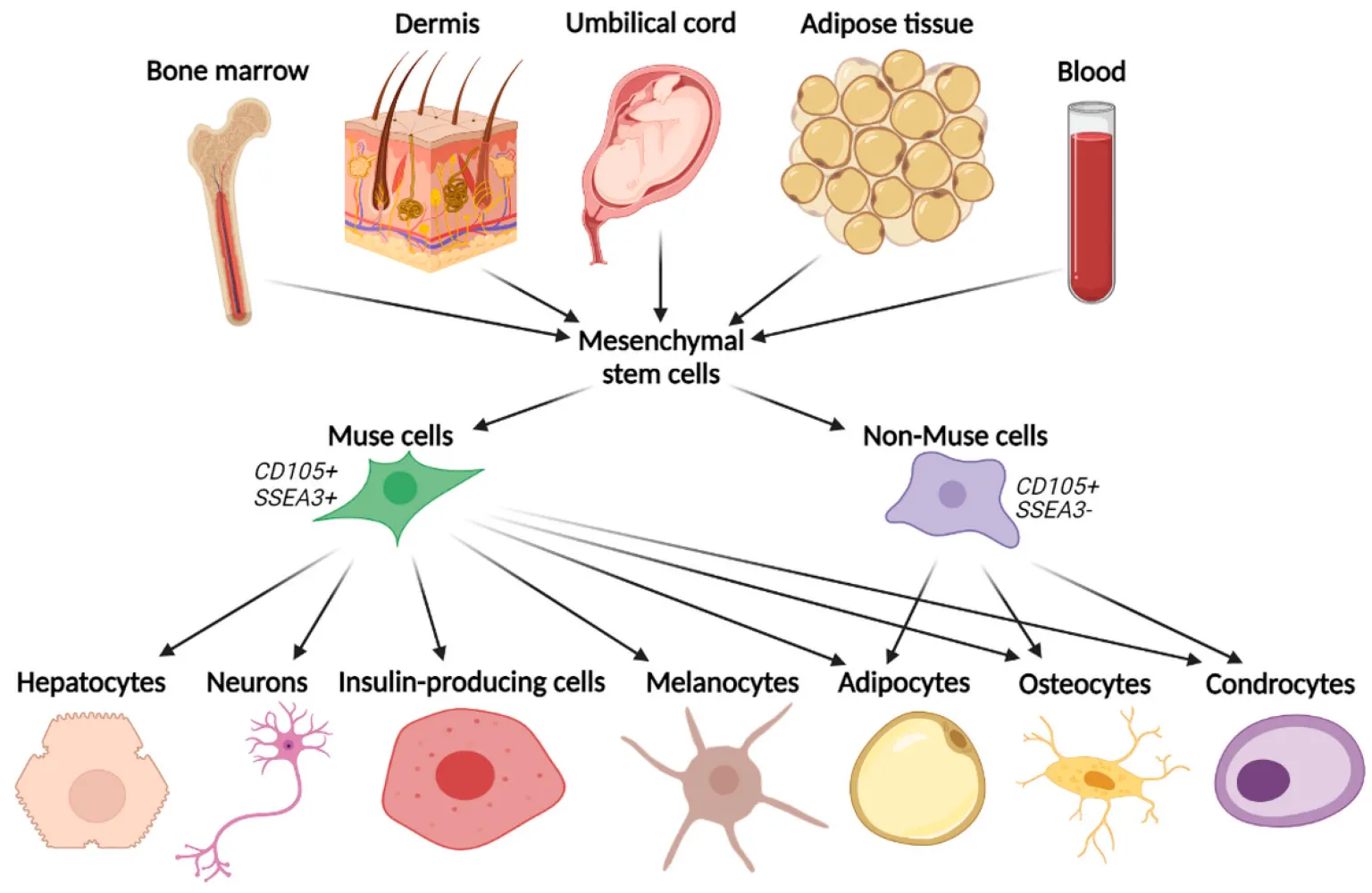
Muse stem cell therapy revolves around the use of multilineage-differentiating stress-enduring (Muse) cells. A mouthful, right? But stick with me, it’s easier than it sounds. Muse cells are a type of stem cell that has an impressive ability to differentiate into multiple cell types, essentially helping to regenerate damaged tissues in the body.
Here’s the magic: Muse cells can survive harsh conditions, making them ideal for use in damaged tissues. They can sense the body’s SOS signals when a tissue is injured, migrating straight to the site of damage, where they work their regenerative magic. Whether it’s heart tissue after a myocardial infarction (fancy way of saying heart attack), the brain after a stroke, or even muscle or skin tissues, these cells have the ability to replace damaged cells, repair the damage, and bring the affected tissues back to life.
What’s really interesting is that Muse cells don’t come with the ethical baggage of embryonic stem cells. While embryonic stem cells are pluripotent and can differentiate into many types of cells, they come with a whole host of issues (like ethical concerns). Muse cells, however, are like the underdog, offering a similar range of abilities without the drama.
Here’s the kicker: Muse cells are naturally found in your body. They are adult stem cells that can be isolated from tissues such as bone marrow, fat tissue, and even the skin. The body actually has these cells in reserve, quietly waiting for the call to action. When there’s damage to the tissues (hello, injury or disease), Muse cells migrate to the injury site, differentiate into the required cell type, and get to work healing.
They were first discovered somewhat accidentally back in 2007 by Japanese scientist Mari Dezawa at Tohoku University in Japan. In one of those classic eureka moments, Dezawa noticed that cells left in a nutrient-free environment overnight survived, unlike most cells that would have perished. These resilient survivors were the Muse cells, and ever since then, researchers have been scrambling to understand just how versatile these little guys really are.
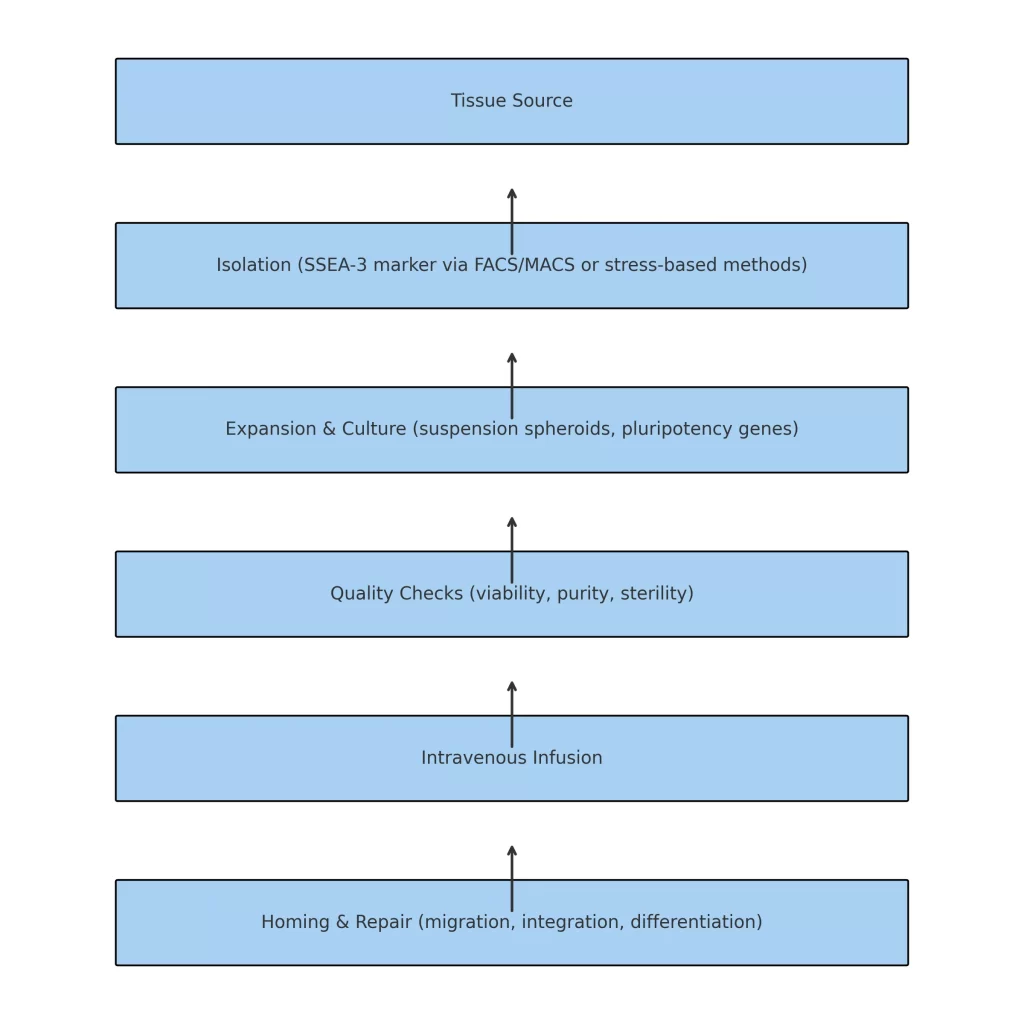
Muse stem cell therapy is a regenerative medicine technique that follows a carefully controlled sequence of steps to ensure that Muse cells are collected, processed, and administered in ways that preserve their therapeutic potential. This process is designed to enhance their ability to support tissue repair, cell regeneration, and overall functional restoration.
Muse cells are sourced from adult human tissues, including bone marrow, adipose tissue (fat), and skin-derived mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs). They are identified by the pluripotency marker SSEA-3 and isolated using precision cell-sorting methods such as Fluorescence-Activated Cell Sorting (FACS) and Magnetic-Activated Cell Sorting (MACS).
In some protocols, Muse cells are enriched through stress-enduring selection methods, where they are exposed to controlled environmental stress that selectively preserves these unique cells while eliminating others.
After isolation, Muse cells are expanded in a GMP-compliant laboratory environment to increase their numbers. They are often cultured in suspension form, where they naturally aggregate into 3D spheroid clusters. This state promotes the expression of key pluripotency-associated genes such as Oct3/4, Sox2, and Nanog, which are essential for their ability to differentiate into multiple cell types.
Before clinical use, Muse cells undergo quality assurance testing to ensure:
Cell viability – confirming the cells are healthy and metabolically active.
Cell purity – verifying a high percentage of genuine Muse cells.
Sterility – ensuring no bacterial, viral, or fungal contamination.
This stringent quality control step guarantees consistency, safety, and optimal performance.
Prepared Muse cells are delivered through intravenous (IV) infusion. Thanks to their unique homing ability, Muse cells can naturally migrate to sites of tissue damage without requiring HLA matching, immune suppression, or preconditioning of the patient.
Once inside the body, Muse cells detect sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) signals emitted by damaged tissues. Guided by these molecular cues, they home to the injury site, integrate into the local tissue microenvironment, and differentiate into cell types compatible with the surrounding tissue—supporting structural repair and functional recovery.
Tissue Collection → SSEA-3 Isolation → Laboratory Expansion → Quality Testing → IV Infusion → Targeted Homing & Repair
At this point, you’re probably wondering, “Okay, Muse cells sound great, but how do they compare to other stem cells like mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs)?”
It’s a fair question, and the difference is worth noting. Let’s break it down:
Both Muse cells and MSCs can differentiate into various cell types, but Muse cells are often considered more potent. While MSCs primarily differentiate into cell types like bone, cartilage, and fat, Muse cells can go even further. They are more like pluripotent cells, meaning they can become a wider range of cell types, including those that help repair the heart, brain, and muscles.
Muse cells have an amazing ability to survive in stressful conditions. They are particularly adept at withstanding harsh environments—like those created by injury or disease. MSCs, while durable, don’t quite have the same resilience under extreme conditions. This makes Muse cells an exciting option for treating serious injuries and diseases where most cells would just give up.
Muse cells are immunomodulatory, which means they can help regulate the immune system. They express HLA-G, a protein that allows them to avoid being attacked by the immune system, something that could make them a game-changer for those who are worried about immune rejection after a stem cell transplant. MSCs can also have immunomodulatory effects, but Muse cells seem to have a bit of an edge here, especially since they can be used without requiring HLA matching, making them a more versatile treatment option.
One of the biggest concerns with stem cell therapy is the potential for tumor formation. Embryonic stem cells and induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) are especially prone to turning into unwanted tumors. Luckily, Muse cells are considered non-tumorigenic—meaning they don’t have the same risk of turning cancerous as other stem cells. This makes them much safer for therapeutic use, as the risk of unwanted growth is minimized.
Both Muse cells and MSCs are being studied for a variety of applications, but Muse cells have shown particular promise in treating neurological diseases (like stroke and spinal cord injuries) and cardiovascular conditions (like heart attack). MSCs, on the other hand, have been more widely researched for their ability to treat musculoskeletal conditions and joint injuries. The difference in their applications largely comes down to their ability to differentiate into a broader range of cell types and better withstand the conditions of more complex organs like the brain and heart.
With their unique ability to differentiate into multiple cell types and repair damaged tissues, Muse cells offer an exciting future in regenerative medicine. Unlike many other stem cell therapies, Muse cells are non-tumorigenic, immune-evasive, and self-renewing—qualities that make them safe and effective in treating some of the most challenging diseases of our time.
From stroke recovery to cardiovascular disease repair, and even potential breakthroughs in spinal cord injuries and skin regeneration, Muse cells are on track to reshape the way we approach healing and recovery.
Now that you’re well-versed in what Muse stem cell treatment is and how it compares to other stem cells, it’s time to dive into some of the real-world applications and clinical trial results that are taking the medical world by storm. We’ll also touch on safety, costs, and everything you should consider before making a decision.
Muse cells are more than just a theoretical concept—they are already being tested in clinical trials, and the results are looking very promising. Let’s take a look at some of the studies that have been carried out to date:
A clinical trial involving 35 stroke patients investigated the efficacy of CL2020, an allogeneic Muse cell-based product, in stroke recovery. The results indicated that 68% of participants experienced significant improvements, enabling them to perform daily activities independently, such as eating, walking, and using public transportation. Additionally, 30% of these patients returned to work post-treatment. These findings suggest that Muse cell therapy can facilitate functional recovery beyond mere survival.
A trial focusing on spinal cord injury patients—people who often face complete paralysis after their injuries—showed improvements in motor function. Participants were able to move their wrists and toes after being treated with Muse cells. While the trial was small (just 10 participants), the results were encouraging enough to pave the way for larger, more extensive studies.
In newborns diagnosed with HIE, a condition caused by a lack of oxygen at birth that can lead to permanent brain damage, Muse cell therapy showed impressive results. In one clinical trial, 66% of babies who received Muse cells had normal developmental scores. That’s nearly double the success rate compared to babies who only received the standard treatment, therapeutic hypothermia (which has a success rate of about 33%). This represents a major breakthrough in neonatal care and has the potential to change the lives of countless children.
So, are Muse cells safe? Here’s some good news: Clinical trials involving Muse stem cell therapy have been conducted with a limited number of patients, and while no serious side effects or tumor formation have been reported in these studies, comprehensive long-term data are still limited.
Promising results in stroke, spinal cord injury, and neonatal brain injury.
High recovery rates and functional improvements in patients.
Safety profile: No tumors or significant side effects reported.
Immunomodulatory effects: Muse cells can be used without requiring HLA matching, making them more versatile.
Currently, Muse stem cell therapy is still in the experimental phase. While it shows promising results in clinical trials, FDA approval is a lengthy process that requires substantial evidence. The therapy is being tested under regulated clinical trial protocols, but it’s not yet an FDA-approved treatment. This means that if you want to undergo this therapy, it will likely be as part of a clinical trial or through clinics that are offering experimental treatments.
If you’re considering Muse stem cell therapy, ensure it’s being conducted by qualified healthcare professionals with experience in regenerative medicine.
Like any medical treatment, there are a few things to keep in mind before diving in:
While Muse cells are generally safe, there are still risks associated with stem cell therapy in general. For example, any procedure that involves injecting cells into the body carries a small risk of infection or other complications, such as reactions to the injection site.
We’ve only seen short-term results so far. The long-term safety and effectiveness of Muse cell therapy will need more research to ensure that the cells continue to function properly in the body over time, and that they don’t lead to any unexpected outcomes (like tumor formation). But as of now, the risk of tumors appears to be very low.
Muse stem cell therapy is still an emerging field, and not all clinics offer it. You may need to travel to specialized centers or participate in clinical trials to access this therapy. Clinics like R3 Stem Cell Mexico are currently offering innovative therapies in regenerative medicine, including Muse stem cell treatments, but it’s essential to do your homework and make sure you’re seeking care from a trusted, experienced provider.
Muse stem cell therapy costs range from $5,000 to $25,000 per treatment, depending on factors such as the clinic location, the type of stem cells used, and the number of sessions required. Prices may also vary based on additional services like lab testing, imaging, and follow-up care.
That depends on your condition and your goals. If you’re dealing with a degenerative disease, stroke, heart disease, or spinal cord injuries, and traditional treatments haven’t worked, Muse stem cell therapy might offer the hope and healing you’re looking for.
Before taking the plunge, though, be sure to:
Consult with a qualified healthcare provider who has experience in regenerative medicine and stem cell therapy.
Consider participating in a clinical trial to gain access to advanced treatments.
Understand the cost and what to expect in terms of treatment duration and long-term effects.
R3 Stem Cell Mexico offers Muse stem cell therapy, which uses pluripotent-like cells derived from mesenchymal stem cells to repair damaged tissues. Patients travel to our clinic in Mexico for advanced regenerative treatments in a certified medical facility with experienced specialists.
Contact US

Dr. David Greene
MD, PhD, MBA
Dr. David Greene, MD, PhD, MBA, is a pioneering leader in regenerative medicine and healthcare marketing. As a residency and fellowship-trained orthopedic surgeon, Dr. Greene transitioned from clinical practice to become the founder and CEO of R3 Stem Cell and US Lead Network, where he has revolutionized patient care and medical practice growth through innovative therapies and digital marketing strategies. He has authored two influential books on healthcare internet marketing, ranks among the top expert authors globally, and has been featured on the cover of Corporate Vision magazine for his impact on global regenerative therapies. Beyond his professional achievements, Dr. Greene is passionate about education, compassion, and continuous innovation.